LeetCode / Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
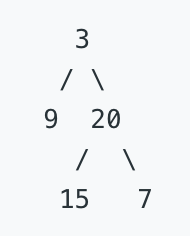
return its minimum depth = 2.
木の深さのMaximumをとる問題はありましたが、今度はMinimumをとる問題です。
maxをminに変えるだけでOK…とは行かないです。
解答・解説
解法1
基本的には、recursiveな関数を定義し1 + min(self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right))で最も浅い木の深さを取得する、という戦略で良いのですが、以下の木のように片方だけsubtreeがない場合、

最も浅い木の深さを取得してしまうと0となりますが、The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.と定義されているので、存在するsubtreeを辿った上で、最も浅い木の深さを返す必要があります。
つまり1 + max(self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right))をとるという条件分岐を加える必要があるということです。
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution: def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: if not root: return 0 elif not root.left or not root.right: return 1 + max(self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right)) else: return 1 + min(self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right))
解法2
Discussionの中で、3 linesのシンプルなコードがあったので転載します。
class Solution: def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: if not root: return 0 d = list(map(self.minDepth, (root.left, root.right))) return 1 + (min(d) or max(d))
self.minDepthをroot.left, root.rightに適用する処理でmap関数を使っていますね。
が、以下記事にあるように、map関数を適用して得られたイテレータをリストに変換する処理でオーバーヘッドが生じ、計算は遅くなるようです。
実際、LeetCodeへのsubmitを何度か行なってみた体感では、map関数を使わない方が速かったです。
また最後のreturn 1 + (min(d) or max(d))の処理について補足すると、
pythonで(a or b)は、aが存在すればa、存在しなければbを返します。(min(d) or max(d))は、min(d) > 0のときにmin(d)、min(d) == 0のときにmax(d)を返します。
解法1で説明したように、片方だけsubtreeがない、つまりmin(d) == 0のときに、存在するsubtreeをたどる、つまり1 + max(d)をとるような処理になっています。